Publications
Click titles to access papers.
Note: Not all papers are publicly available. Publisher subscriptions may be needed.
In Press & ArXiv

23. Digital defocus aberration interference for automated optical microscopy
Haowen Zhou*, Shi Zhao*, Yujie Fan, Zhenyu Dong, Oumeng Zhang, Viviana Gradinaru, Changhuei Yang
ArXiv, 2025 (BibTex) [Project Page]
We recently discovered a phenomenon that the digitally summed Fourier spectrum of two images acquired from two-angle illumination exhibits interference-like fringe modulation when the sample is out-of-focus. These digital fringes correlate directly with defocus through a physics-based relation. Based on this principle, we developed an automatic, efficient, and generalizable defocus detection method termed digital defocus aberration interference (DAbI).
Haowen Zhou*, Shi Zhao*, Yujie Fan, Zhenyu Dong, Oumeng Zhang, Viviana Gradinaru, Changhuei Yang
ArXiv, 2025 (BibTex) [Project Page]
We recently discovered a phenomenon that the digitally summed Fourier spectrum of two images acquired from two-angle illumination exhibits interference-like fringe modulation when the sample is out-of-focus. These digital fringes correlate directly with defocus through a physics-based relation. Based on this principle, we developed an automatic, efficient, and generalizable defocus detection method termed digital defocus aberration interference (DAbI).
2025
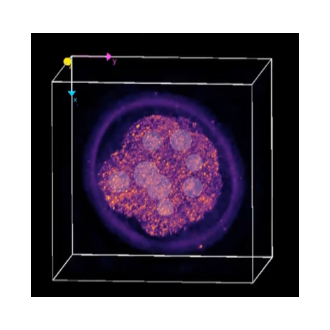
22. Analytic Fourier ptychotomography for aberration-free and high-resolution volumetric refractive index imaging
Zhenyu Dong*, Haowen Zhou*, Ruizhi Cao*, Oumeng Zhang, Shi Zhao, Panlang Lyu, Reinaldo E Alcalde, Changhuei Yang
Nature Communications (BibTex) [Project Page]
We propose Analytic Fourier Ptychotomography (AFP), a computational microscopy technique that analytically reconstructs aberration-free, complex-valued 3D RI distributions without iterative optimization or axial scanning.
Zhenyu Dong*, Haowen Zhou*, Ruizhi Cao*, Oumeng Zhang, Shi Zhao, Panlang Lyu, Reinaldo E Alcalde, Changhuei Yang
Nature Communications (BibTex) [Project Page]
We propose Analytic Fourier Ptychotomography (AFP), a computational microscopy technique that analytically reconstructs aberration-free, complex-valued 3D RI distributions without iterative optimization or axial scanning.
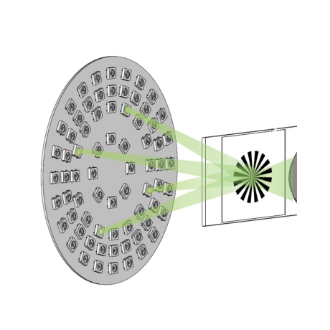
21. Hybrid-illumination multiplexed Fourier ptychographic microscopy with robust aberration correction
Shi Zhao, Haowen Zhou, Changhuei Yang
Journal of Physics: Photonics, 2025 (BibTex) [GitHub]
We propose Hybrid-illumination Multiplexed Fourier Ptychographic Microscopy (HMFPM), an advanced computational imaging framework, that integrates the advantages of multiplexed FPM and analytic reconstruction methods.
Shi Zhao, Haowen Zhou, Changhuei Yang
Journal of Physics: Photonics, 2025 (BibTex) [GitHub]
We propose Hybrid-illumination Multiplexed Fourier Ptychographic Microscopy (HMFPM), an advanced computational imaging framework, that integrates the advantages of multiplexed FPM and analytic reconstruction methods.
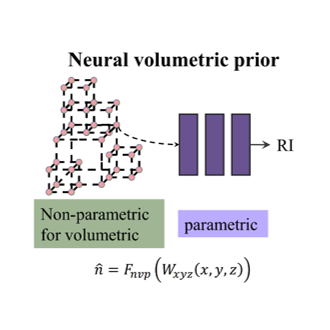
20. Recover biological structure from sparse-view diffraction images with neural volumetric prior
Renzhi He, Haowen Zhou, Yi Xue
ICCV, 2025 (BibTex) [Project Page]
We develop Neural Volumetric Prior (NVP) for high-fidelity volumetric reconstruction of semi-transparent biological samples from sparse-view microscopic images. NVP integrates explicit and implicit neural representations and incorporates the physical prior of diffractive optics.
Renzhi He, Haowen Zhou, Yi Xue
ICCV, 2025 (BibTex) [Project Page]
We develop Neural Volumetric Prior (NVP) for high-fidelity volumetric reconstruction of semi-transparent biological samples from sparse-view microscopic images. NVP integrates explicit and implicit neural representations and incorporates the physical prior of diffractive optics.
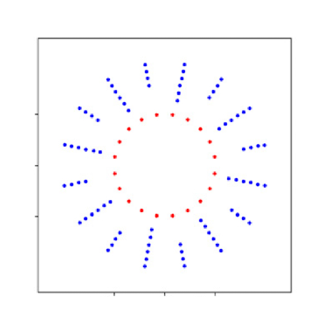
19. Dome-APIC illumination design for high space-bandwidth product analytic imaging
Siyu (Steven) Lin, Haowen Zhou, Ruizhi Cao, Shi Zhao, Oumeng Zhang, Changhuei Yang
Biomedical Optics Express, 2025 (BibTex)
We introduce an illumination framework tailored for Angular Ptychographic Imaging with Close-form method (APIC) consisting of a distant annular LED ring and an LED dome that enables the reconstruction of a larger area with an extended synthetic numerical aperture, consequently enhancing resolution.
Siyu (Steven) Lin, Haowen Zhou, Ruizhi Cao, Shi Zhao, Oumeng Zhang, Changhuei Yang
Biomedical Optics Express, 2025 (BibTex)
We introduce an illumination framework tailored for Angular Ptychographic Imaging with Close-form method (APIC) consisting of a distant annular LED ring and an LED dome that enables the reconstruction of a larger area with an extended synthetic numerical aperture, consequently enhancing resolution.

18. Single-shot volumetric fluorescence imaging with neural fields
Oumeng Zhang*, Haowen Zhou*, Brandon Y Feng, Elin M Larsson, Reinaldo E Alcalde, Siyuan Yin, Catherine Deng, Changhuei Yang
Advanced Photonics, 2025 (BibTex) [Project Page]
Single-shot volumetric fluorescence imaging captures biological processes with high temporal resolution and a large field of view, unlike traditional methods requiring multiple axial plane scans. The paper introduces a QuadraPol PSF combined with neural fields, using a compact custom polarizer and a polarization camera to detect fluorescence and encode the 3D scene within a compact PSF without depth ambiguity. This approach significantly reduces acquisition time by approximately 20 times and captures a 100 mm³ volume in one shot, demonstrated through imaging bacterial colonies and plant root morphology.
Oumeng Zhang*, Haowen Zhou*, Brandon Y Feng, Elin M Larsson, Reinaldo E Alcalde, Siyuan Yin, Catherine Deng, Changhuei Yang
Advanced Photonics, 2025 (BibTex) [Project Page]
Single-shot volumetric fluorescence imaging captures biological processes with high temporal resolution and a large field of view, unlike traditional methods requiring multiple axial plane scans. The paper introduces a QuadraPol PSF combined with neural fields, using a compact custom polarizer and a polarization camera to detect fluorescence and encode the 3D scene within a compact PSF without depth ambiguity. This approach significantly reduces acquisition time by approximately 20 times and captures a 100 mm³ volume in one shot, demonstrated through imaging bacterial colonies and plant root morphology.

17. Impact of stain variation and color normalization for prognostic predictions in pathology
Siyu Lin, Haowen Zhou, Mark Watson, Ramaswamy Govindan, Richard J. Cote, Changhuei Yang
Scientific Reports, 2025 (BibTex)
We show that a well-trained DNN model trained on one batch of histological slides failed to generalize to another batch prepared at a different time from the same tissue blocks, even when stain normalization methods were applied. The impact of color consistenct will affect the generalization issues in deep learning for digital pathology studies.
Siyu Lin, Haowen Zhou, Mark Watson, Ramaswamy Govindan, Richard J. Cote, Changhuei Yang
Scientific Reports, 2025 (BibTex)
We show that a well-trained DNN model trained on one batch of histological slides failed to generalize to another batch prepared at a different time from the same tissue blocks, even when stain normalization methods were applied. The impact of color consistenct will affect the generalization issues in deep learning for digital pathology studies.
2024
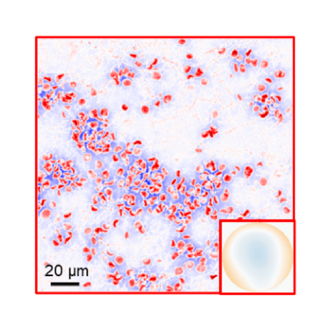
16. Efficient, gigapixel-scale, aberration-free whole slide scanner using angular ptychographic imaging with closed-form solution
Shi Zhao*, Haowen Zhou*, Siyu Lin, Ruizhi Cao, Changhuei Yang
Biomendical Optics Express, 2024 (BibTex) [Code & Data]
We report a whole slide imaging system based on angular ptychographic imaging with a closed-form solution (WSI-APIC), which offers efficient, tens-of-gigapixels, large-FOV, aberration-free imaging. We customize the optical system design for pathology slide scanning and boost the algorithm with GPU-acceleration.
Shi Zhao*, Haowen Zhou*, Siyu Lin, Ruizhi Cao, Changhuei Yang
Biomendical Optics Express, 2024 (BibTex) [Code & Data]
We report a whole slide imaging system based on angular ptychographic imaging with a closed-form solution (WSI-APIC), which offers efficient, tens-of-gigapixels, large-FOV, aberration-free imaging. We customize the optical system design for pathology slide scanning and boost the algorithm with GPU-acceleration.
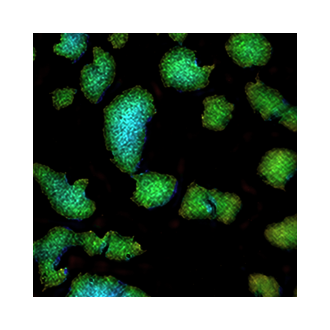
15. Investigating 3D microbial community dynamics of the rhizosphere using quantitative phase and fluorescence microscopy
Oumeng Zhang*, Reinaldo E Alcalde*, Haowen Zhou, Siyuan Yin, Dianne K Newman, Changhuei Yang
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), 2024 (BibTex)
We introduce complex-field and fluorescence microscopy using the aperture scanning technique (CFAST), an innovative imaging system merging three-dimensional (3D) fluorescence with quantitative phase imaging. CFAST’s exceptional depth of field enables efficient 3D volume scanning, reducing bleaching risks associated with traditional fluorescence imaging. Its noninvasive approach facilitates observing interactions and gene expression within and among bacterial taxa, even those not yet genetically tractable.
Oumeng Zhang*, Reinaldo E Alcalde*, Haowen Zhou, Siyuan Yin, Dianne K Newman, Changhuei Yang
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), 2024 (BibTex)
We introduce complex-field and fluorescence microscopy using the aperture scanning technique (CFAST), an innovative imaging system merging three-dimensional (3D) fluorescence with quantitative phase imaging. CFAST’s exceptional depth of field enables efficient 3D volume scanning, reducing bleaching risks associated with traditional fluorescence imaging. Its noninvasive approach facilitates observing interactions and gene expression within and among bacterial taxa, even those not yet genetically tractable.

14. Length-scale study in deep learning prediction for non-small cell lung cancer brain metastasis
Haowen Zhou, Siyu Lin, Mark Watson, Cory T. Bernadt, Oumeng Zhang, Ling Liao, Ramaswamy Govindan, Richard J. Cote, Changhuei Yang
Scientific Reports, 2024 (BibTex)
As deep neural network (DNN) architectures grow in size and complexity, their explainability decreases, posing challenges in interpreting pathology features for broader clinical insights into physiological diseases. To better assess the interpretability of digital microscopic images and guide future microscopic system design, we developed a novel method to study the predictive feature length-scale that underpins a DNN’s predictive power.
Haowen Zhou, Siyu Lin, Mark Watson, Cory T. Bernadt, Oumeng Zhang, Ling Liao, Ramaswamy Govindan, Richard J. Cote, Changhuei Yang
Scientific Reports, 2024 (BibTex)
As deep neural network (DNN) architectures grow in size and complexity, their explainability decreases, posing challenges in interpreting pathology features for broader clinical insights into physiological diseases. To better assess the interpretability of digital microscopic images and guide future microscopic system design, we developed a novel method to study the predictive feature length-scale that underpins a DNN’s predictive power.
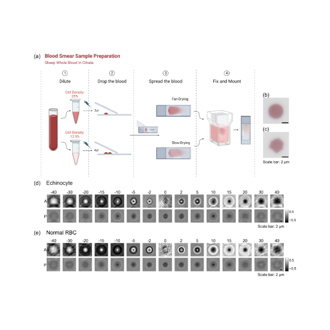
13. Can deep neural networks work with amplitude and phase input of defocused images?
Siyuan Yin, Ruizhi Cao, Mingshu Liang, Cheng Shen, Haowen Zhou, Oumeng Zhang, Changhuei Yang
Optics Express, 2024 Editor's Pick (BibTex)
We assess the feasibility of employing neural networks to directly process full amplitude and phase data from a defocus plane without digital refocusing. Our specific focus lies in understanding the tolerance for defocus in image classification neural networks when amplitude and phase are taken as inputs.
Siyuan Yin, Ruizhi Cao, Mingshu Liang, Cheng Shen, Haowen Zhou, Oumeng Zhang, Changhuei Yang
Optics Express, 2024 Editor's Pick (BibTex)
We assess the feasibility of employing neural networks to directly process full amplitude and phase data from a defocus plane without digital refocusing. Our specific focus lies in understanding the tolerance for defocus in image classification neural networks when amplitude and phase are taken as inputs.
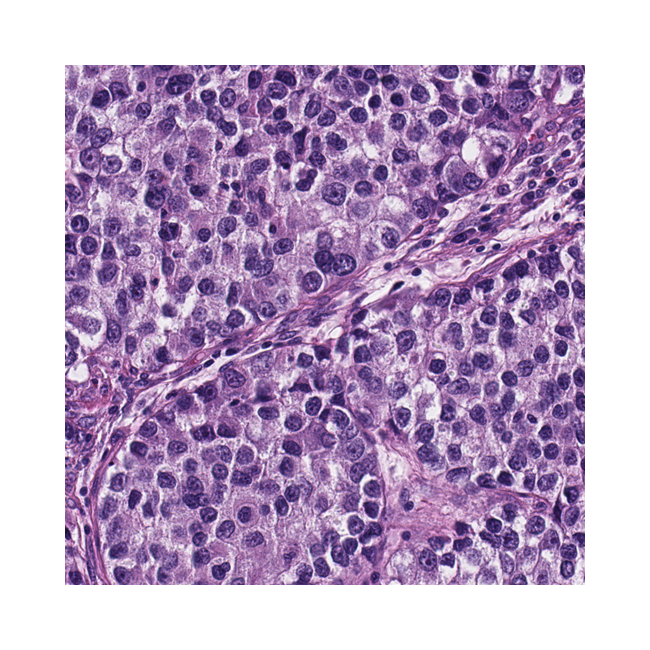
12. AI-guided histopathology predicts brain metastasis in lung cancer patients
Haowen Zhou*, Mark Watson*, Cory T. Bernadt, Steven (Siyu) Lin, Chieh-yu Lin, Jon H. Ritter, Alexander Wein, Simon Mahler, Sid Rawal, Ramaswamy Govindan, Changhuei Yang, Richard J. Cote
Journal of Pathology, 2024 (BibTex) [Code] {Data} News
Brain metastases can occur in nearly half of patients with early and locally advanced (stage I–III) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). There are no reliable histopathologic or molecular means to identify those who are likely to develop brain metastases. We sought to determine if deep learning could be applied to routine H&E-stained primary tumor tissue sections from stage I–III NSCLC patients to predict the development of brain metastasis.
Haowen Zhou*, Mark Watson*, Cory T. Bernadt, Steven (Siyu) Lin, Chieh-yu Lin, Jon H. Ritter, Alexander Wein, Simon Mahler, Sid Rawal, Ramaswamy Govindan, Changhuei Yang, Richard J. Cote
Journal of Pathology, 2024 (BibTex) [Code] {Data} News
Brain metastases can occur in nearly half of patients with early and locally advanced (stage I–III) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). There are no reliable histopathologic or molecular means to identify those who are likely to develop brain metastases. We sought to determine if deep learning could be applied to routine H&E-stained primary tumor tissue sections from stage I–III NSCLC patients to predict the development of brain metastasis.
2023

11. FPM-INR: Fourier ptychographic microscopy image stack reconstruction using implicit neural representations
Haowen Zhou*, Brandon Y. Feng*, Haiyun Guo, Siyu Lin, Mingshu Liang, Christopher A. Metzler, Changhuei Yang
Optica, 2023 (BibTex) [Project Page] {Data}
Fourier ptychographic microscope faces challenges with long image stack reconstruction time and huge data volumes. We designed physics-based neural signal representations to tackle these challenges and facilitates remote diagnosis, and efficient data packaging.
Haowen Zhou*, Brandon Y. Feng*, Haiyun Guo, Siyu Lin, Mingshu Liang, Christopher A. Metzler, Changhuei Yang
Optica, 2023 (BibTex) [Project Page] {Data}
Fourier ptychographic microscope faces challenges with long image stack reconstruction time and huge data volumes. We designed physics-based neural signal representations to tackle these challenges and facilitates remote diagnosis, and efficient data packaging.
2022
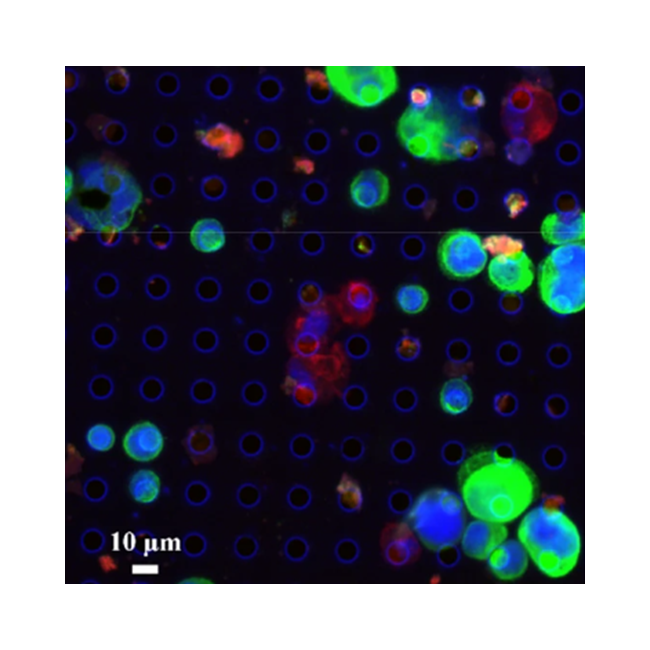
10. Automatic detection of circulating tumor cells and cancer associated fibroblasts using deep learning
Cheng Shen, Siddarth Rawal, Rebecca Brown, Haowen Zhou, Ashutosh Agarwal, Mark A. Watson, Richard J. Cote, Changhuei Yang
Sci. Rep., 2022 (BibTex)
We build an all-in-focus fluorescent microscope for circulating tumor cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts detections. The system outperforms the commercialized microscope systems and achieves high performances in cell counting.
Cheng Shen, Siddarth Rawal, Rebecca Brown, Haowen Zhou, Ashutosh Agarwal, Mark A. Watson, Richard J. Cote, Changhuei Yang
Sci. Rep., 2022 (BibTex)
We build an all-in-focus fluorescent microscope for circulating tumor cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts detections. The system outperforms the commercialized microscope systems and achieves high performances in cell counting.
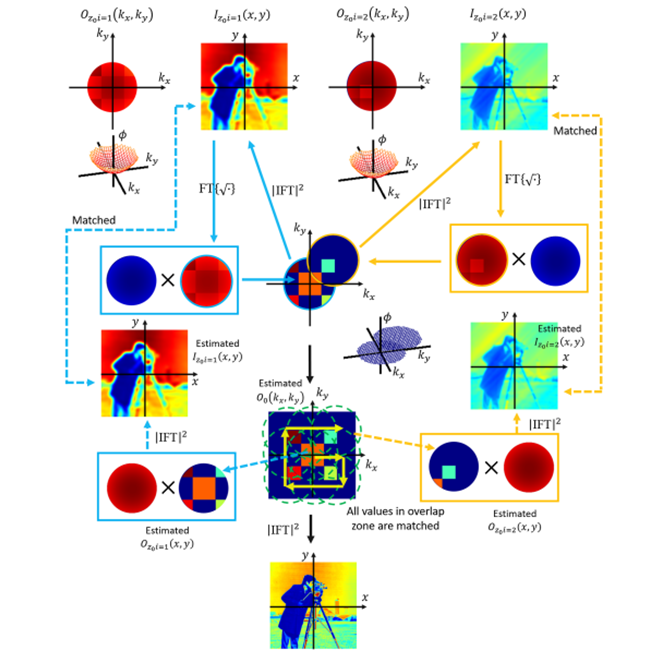
9. Analysis of postreconstruction digital refocusing in Fourier ptychographic microscopy
Haowen Zhou, Cheng Shen, Mingshu Liang, Changhuei Yang
Opt. Eng., 2022 (BibTex)
We applied a thorough analysis in digital refocusing mechanism for Fourier ptychographic microscopy. It explains why a simple propagation physical model cannot succeed in a post-reconstrution manner.
Haowen Zhou, Cheng Shen, Mingshu Liang, Changhuei Yang
Opt. Eng., 2022 (BibTex)
We applied a thorough analysis in digital refocusing mechanism for Fourier ptychographic microscopy. It explains why a simple propagation physical model cannot succeed in a post-reconstrution manner.
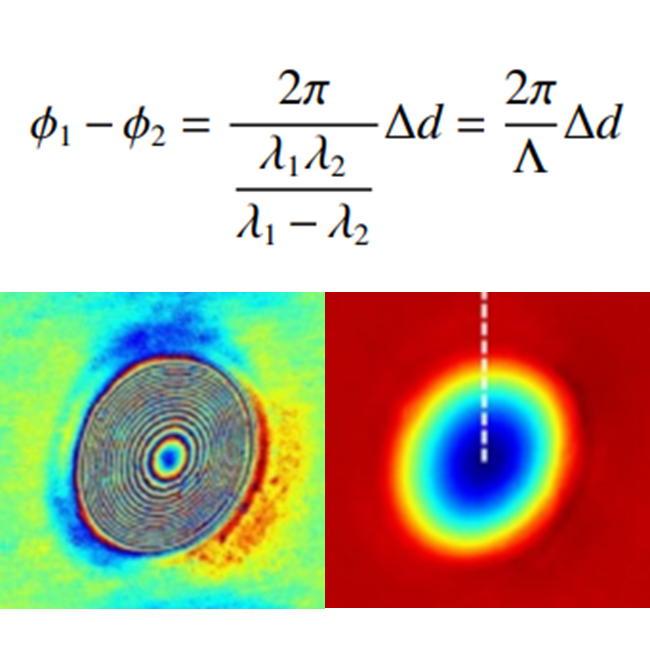
8. A review of the dual-wavelength technique for phase imaging and 3D topography
Haowen Zhou, Mallik Hussain, Partha P. Banerjee
Light Adv. Manuf., 2022 (BibTex)
We surveyed dual-wavelength technique in phase imaging and 3D topography and summarized the current challenges in this field.
Haowen Zhou, Mallik Hussain, Partha P. Banerjee
Light Adv. Manuf., 2022 (BibTex)
We surveyed dual-wavelength technique in phase imaging and 3D topography and summarized the current challenges in this field.
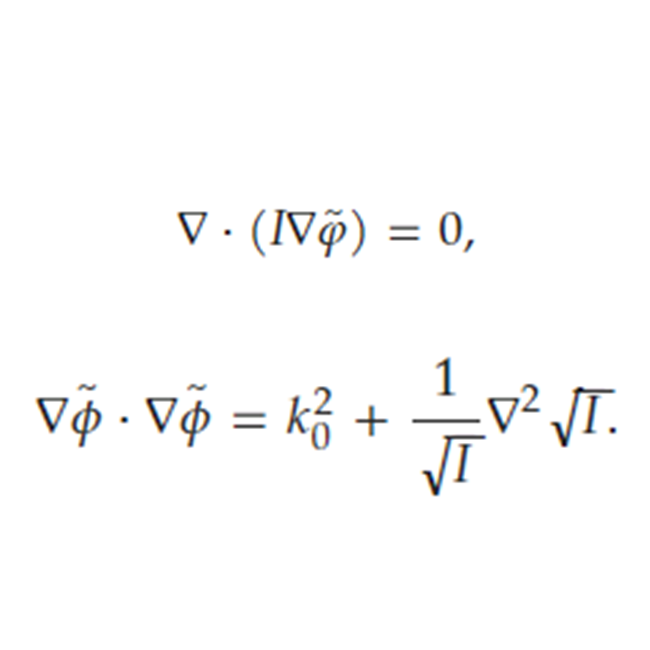
7. Non-recursive transport of intensity phase retrieval with the transport of phase
Haowen Zhou, Haiyun Guo, Partha P. Banerjee
Appl. Opt., 2022 Editor's Pick (BibTex)
Transport of phase equation is a twin equation with transport of intensity equation, derived from the Helmholtz equation. The two equations can demonstrate the entire complex optical field and help amplitude-phase imaging.
Haowen Zhou, Haiyun Guo, Partha P. Banerjee
Appl. Opt., 2022 Editor's Pick (BibTex)
Transport of phase equation is a twin equation with transport of intensity equation, derived from the Helmholtz equation. The two equations can demonstrate the entire complex optical field and help amplitude-phase imaging.

6. Use of structured light in 3D reconstruction of transparent objects
Haiyun Guo, Haowen Zhou, Partha P. Banerjee
Appl. Opt., 2022 (BibTex)
A simple concept of light refraction due to a change of refractive index and curvature of the interface provides a straightforward way to reconstruct transparent phase objects with projected structured light.
Haiyun Guo, Haowen Zhou, Partha P. Banerjee
Appl. Opt., 2022 (BibTex)
A simple concept of light refraction due to a change of refractive index and curvature of the interface provides a straightforward way to reconstruct transparent phase objects with projected structured light.
2021
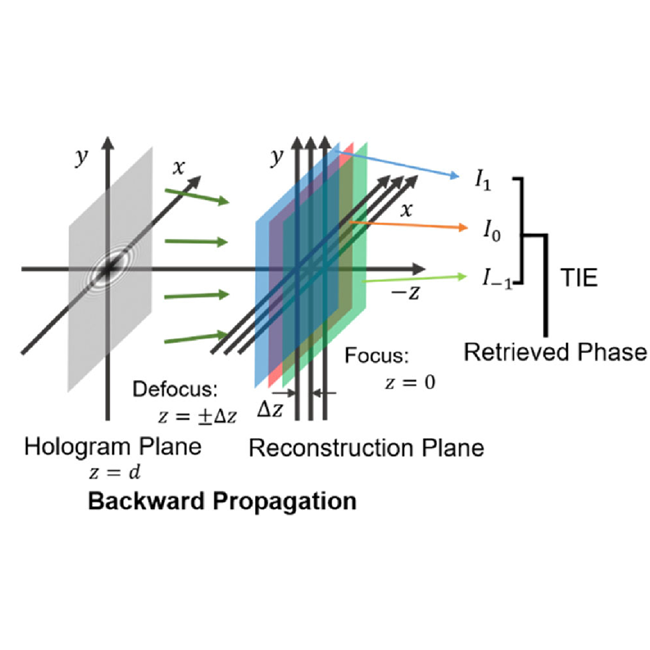
5. Performance analysis of phase retrieval using transport of intensity with digital holography [Invited]
Haowen Zhou, Elena Stoykova, Mallik Hussain, Partha P. Banerjee
Appl. Opt., 2021 (BibTex)
Transport of intensity equation can facilitate wrapping free phase retrieval for digital holography. We compares its performance with traditional off-axis single- and dual-wavelength techniques.
Haowen Zhou, Elena Stoykova, Mallik Hussain, Partha P. Banerjee
Appl. Opt., 2021 (BibTex)
Transport of intensity equation can facilitate wrapping free phase retrieval for digital holography. We compares its performance with traditional off-axis single- and dual-wavelength techniques.
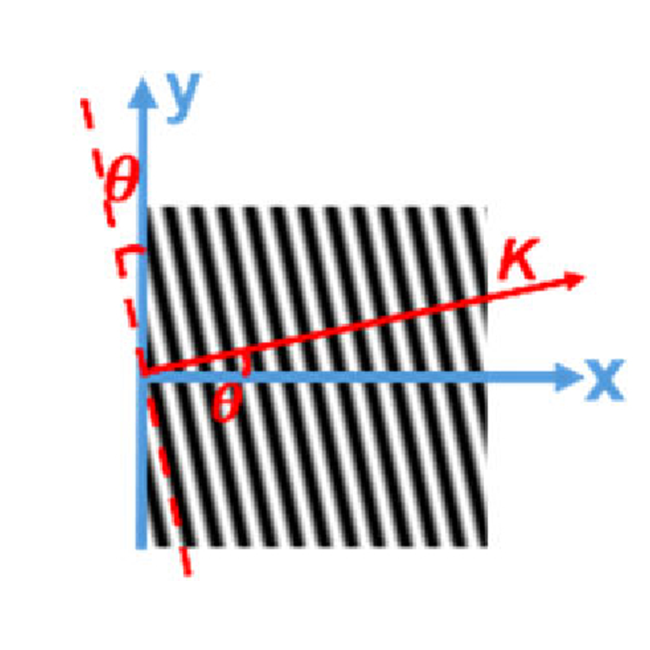
4. Single-shot digital phase-shifting Moiré patterns for 3D topography
Haiyun Guo, Haowen Zhou, Partha P. Banerjee
Appl. Opt., 2021 (BibTex)
We demonstrates a simple and robust technique of Moiré topography with single-image capture and incorporating digital filtering along with a four-step digitally implemented phase-shifting method for 3D surface mapping.
Haiyun Guo, Haowen Zhou, Partha P. Banerjee
Appl. Opt., 2021 (BibTex)
We demonstrates a simple and robust technique of Moiré topography with single-image capture and incorporating digital filtering along with a four-step digitally implemented phase-shifting method for 3D surface mapping.
2019
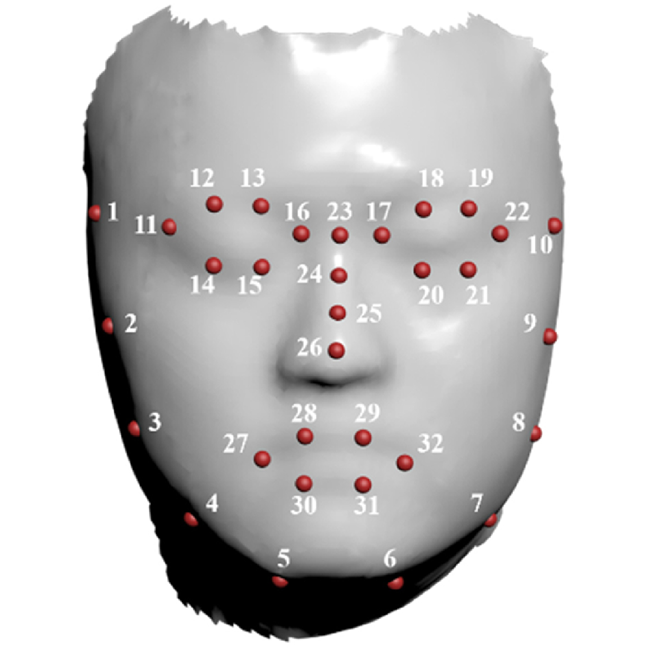
3. Digital correlation of computer-generated holograms for 3D face recognition
Haowen Zhou, Xiaomeng Sui, Liangcai Cao, Partha P. Banerjee
Appl. Opt., 2019 (BibTex)
A digital correlation method of a computer-generated hologram (CGH) can encode 3D spatial data information into a 2D hologram. We demonstrate its application in for 3D face recognition.
Haowen Zhou, Xiaomeng Sui, Liangcai Cao, Partha P. Banerjee
Appl. Opt., 2019 (BibTex)
A digital correlation method of a computer-generated hologram (CGH) can encode 3D spatial data information into a 2D hologram. We demonstrate its application in for 3D face recognition.
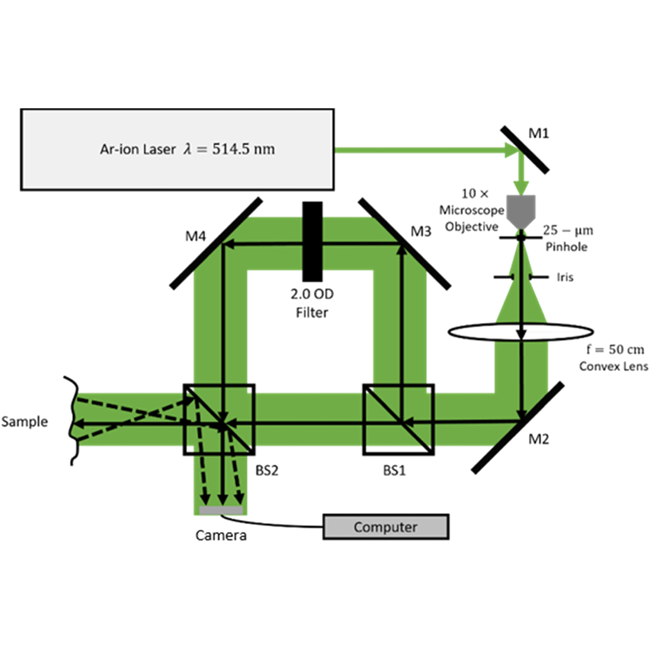
2. 3D object recognition through processing of 2D holograms
Behzad Bordbar, Haowen Zhou, Partha P. Banerjee
Appl. Opt., 2019 (BibTex)
Digitally recorded holograms encode three-dimensional obejct information into a 2D images (hologram). This work demonstrates the correlation of the holograms as metric to reveal object topographic features.
Behzad Bordbar, Haowen Zhou, Partha P. Banerjee
Appl. Opt., 2019 (BibTex)
Digitally recorded holograms encode three-dimensional obejct information into a 2D images (hologram). This work demonstrates the correlation of the holograms as metric to reveal object topographic features.
2018
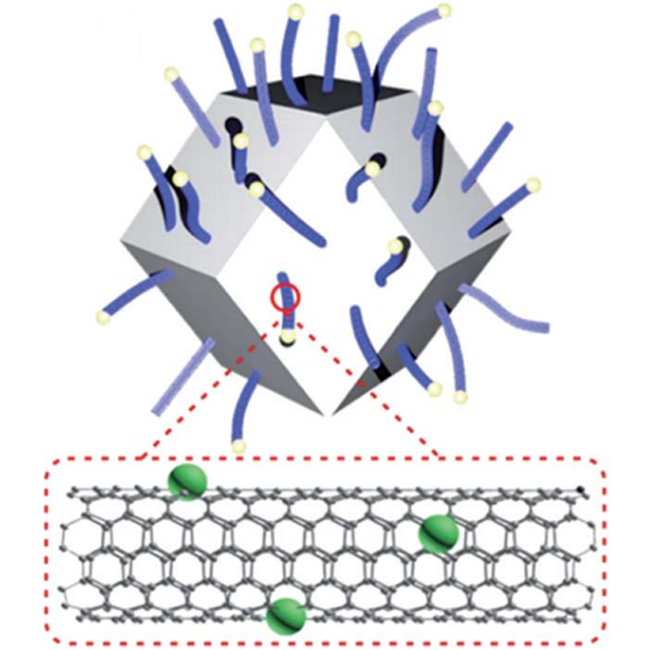
1. Sulfur dioxide gas-sensitive materials based on zeolitic imidazolate framework-derived carbon nanotubes
Qun Li*, Jiabin Wu*, Liang Huang, Junfeng Gao, Haowen Zhou, Yijie Shi, Qinhe Pan, Gang Zhang, Yu Du, Wenxi Liang
J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018 (BibTex)
We demonstrate the synthesis of gas-sensing materials for sulfur dioxide (ZIF-67), which results in significant sensitivity, cross-selectivity and durability towards SO2 at room temperature.
Qun Li*, Jiabin Wu*, Liang Huang, Junfeng Gao, Haowen Zhou, Yijie Shi, Qinhe Pan, Gang Zhang, Yu Du, Wenxi Liang
J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018 (BibTex)
We demonstrate the synthesis of gas-sensing materials for sulfur dioxide (ZIF-67), which results in significant sensitivity, cross-selectivity and durability towards SO2 at room temperature.
